Preventive maintenance (PM) is a proactive approach aimed at ensuring equipment operates at peak performance through scheduled maintenance and repairs. Its importance lies in enhancing operational efficiency, extending equipment lifespan, and preventing costly breakdowns and downtime. By implementing a well-designed PM program, regulated manufacturers can optimize their operations and minimize maintenance-related risks. And this post will detail how that looks.
First, an important distinction.
The Difference Between Preventive and Reactive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance differs from reactive maintenance.
- Preventive maintenance is a proactive approach that involves scheduled inspections and upkeep to prevent failures before they happen. It minimizes breakdowns and optimizes equipment performance.
- Reactive maintenance deals with fixing equipment failures as they occur, often resulting in unplanned downtime and increased repair costs.
Preventive maintenance minimizes the likelihood of unexpected failures by regularly servicing equipment according to a predetermined schedule, reducing maintenance costs and operational disruptions.
The Basics of Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance entails a series of processes, guidelines, and tools for maintaining equipment and assets in optimal condition. Proactively addressing potential issues aims to prevent unplanned failures and minimize downtime while increasing asset reliability and maximizing the impact of costs and labor available resources.
The first step in creating a preventive maintenance program is identifying your company’s specific maintenance requirements. This involves assessing the scope of your maintenance program, listing all equipment requiring maintenance, and determining their importance to daily operations.
By understanding maintenance needs, regulated manufacturers can effectively allocate resources, set priorities, and develop a targeted maintenance strategy.
Establishing Preventative Maintenance Goals and Priorities
Manufacturers should identify specific objectives, such as reducing downtime, increasing reliability, or cutting costs. Prioritizing goals helps focus attention and resources on areas that will have the greatest impact on operational efficiency.
Developing detailed maintenance procedures is essential to doing this effectively. This entails creating a comprehensive plan that outlines all maintenance tasks required to maintain company assets. By defining procedures and distributing them among maintenance personnel, regulated manufacturers ensure consistency and effectiveness in operations. Additionally, defining necessary resources, tooling, and parts streamlines maintenance processes and minimizes downtime.
A well-planned maintenance schedule is critical for executing preventive maintenance effectively. Utilizing factors such as manufacturer recommendations,and historical data, and professional advice, regulated manufacturers can develop a schedule that minimizes downtime and maintenance costs while ensuring equipment operates reliably. By adhering to a structured maintenance schedule, companies can optimize equipment performance and maximize operational efficiency.
Once goals are established, manufacturers should define and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge the success of the preventive maintenance program. KPIs such as preventive maintenance compliance, overall equipment effectiveness, and mean time between failure provide valuable insights into maintenance performance and efficiency.
By establishing specific, attainable performance objectives and selecting relevant KPIs, such as equipment uptime and mean time between failures (MTBF), regulated manufacturers can monitor program progress and identify areas for improvement. Clear performance targets enable companies to make data-driven decisions to enhance operational performance.
Total buy-in from all stakeholders is essential to the success of a preventive maintenance program. Engaging maintenance managers, technicians, and other team members in the planning process ensures everyone is aligned with the program’s goals and responsibilities. Effective communication and collaboration are essential for implementing a successful preventive maintenance strategy.

Leveraging Technology and Software Solutions
Technology plays a critical role in modern preventive maintenance programs. Regulated mManufacturers can leverage advanced software solutions, such as computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), to streamline maintenance processes, schedule inspections, and track maintenance activities. The right technology improves efficiency, accuracy, and visibility into maintenance operations—and a CMMS is a perfect fit.
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is instrumental in managing a preventive maintenance program. It streamlines maintenance tasks, schedules work orders, and monitors equipment performance, enhancing maintenance program efficiency and effectiveness.
With features like asset management and real-time monitoring, CMMS software facilitates data-driven decision-making and enables regulated manufacturers to optimize maintenance operations.
Accurate triggers are essential for effective preventive maintenance scheduling. Manufacturers should consider factors such as equipment usage, performance history, and criticality when setting up maintenance triggers. Automated scheduling helps ensure that maintenance tasks are completed on time and according to schedule.
Proper training is essential for effectively implementing a preventive maintenance program. Manufacturers should train maintenance workers to perform preventive maintenance tasks, use maintenance software, and follow established procedures. Pilot programs can help teams adjust to new processes and identify areas for improvement.
Once the preventive maintenance program is implemented, manufacturers should analyze results and track KPIs to assess its effectiveness. Comparing performance metrics against benchmarks helps identify areas for improvement and optimization. Continuous feedback and adjustments ensure the preventive maintenance program remains efficient and sustainable.
Monitoring and Improving Your Program
Continuous monitoring and improvement help regulated manufacturers identify areas for enhancement and ensure program alignment with goals and objectives. Continuous improvement efforts enable companies to adapt to changing operational needs, optimize maintenance processes, and sustain long-term program effectiveness.
Keeping things running smoothly requires some key components to maximize equipment reliability and operational efficiency, namely Standard Operating Procedures, Maintenance Scheduling, and Strategies.
By focusing on standard operating procedures (SOPs), maintenance schedules, and proactive maintenance strategies, companies can establish robust maintenance protocols to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive SOPs outline step-by-step instructions for performing maintenance tasks, ensuring consistency and adherence to best practices across maintenance operations. These procedures cover various aspects of equipment maintenance, including inspection, lubrication, calibration, and repair, providing maintenance personnel with clear guidance for task execution. By standardizing maintenance procedures, regulated manufacturers can minimize errors, enhance safety, and maintain equipment integrity.
Effective maintenance scheduling minimizes disruptions to production processes. Regulated manufacturers must develop a structured maintenance schedule based on equipment criticality, usage patterns, and regulatory requirements.
By integrating historical maintenance data, manufacturer recommendations, and operational insights, companies can create a proactive maintenance schedule that balances maintenance frequency with operational demands. This helps companies anticipate maintenance needs and optimize resource allocation.
Different Maintenance Strategies
Adopting proactive maintenance strategies is always preferable as they prevent equipment failures and minimize downtime. The focus is on identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into costly failures, thereby enhancing equipment reliability and operational continuity.
However, regulated manufacturers can implement various maintenance techniques to ensure their planning is covered throughout the lifespan of various pieces of equipment. This includes predictive, preventive, and corrective classifications. Understanding these maintenance tasks and their respective roles is essential for developing a comprehensive maintenance strategy tailored to regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Predictive maintenance involves using data analytics, sensor technology, and machine learning algorithms to anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance activities accordingly.
This approach relies on condition monitoring techniques, such as vibration analysis, thermography, and oil analysis, to assess the health and performance of critical assets in real-time.
Preventive maintenance focuses on scheduled inspections, routine servicing, and component replacements aimed at preventing equipment failures and optimizing performance. Unlike predictive maintenance, which relies on predictive analytics, preventive maintenance follows a predetermined maintenance schedule based on equipment manufacturer recommendations, historical maintenance data, and regulatory requirements.
Preventive maintenance, which involves regular maintenance tasks such as lubrication, calibration, and cleaning, minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns and ensures equipment operates at peak efficiency.
And then there’s corrective maintenance, also known as reactive maintenance. This involves addressing equipment failures or malfunctions after they occur. While corrective maintenance is typically associated with unplanned downtime and emergency repairs, it remains a crucial component of a comprehensive maintenance strategy for regulated manufacturers and requires pre-planning from a procedural standpoint.
Despite its reactive nature, corrective maintenance is vital in restoring equipment functionality, minimizing production losses, and mitigating safety risks. However, reliance on corrective maintenance alone can lead to increased downtime, higher maintenance costs, and non-compliance with regulatory mandates. Therefore, regulated manufacturers should prioritize preventive and predictive maintenance activities to reduce the frequency and impact of corrective interventions.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance Programs
Here are some key benefits of preventive maintenance programs:
Enhanced Asset Performance
Preventive maintenance programs are designed to keep equipment operating at peak performance through regular inspections, servicing, and component replacements. They help regulated manufacturers maintain the reliability and efficiency of critical assets by addressing potential issues before they escalate into major failures. This proactive approach minimizes unexpected downtime, production disruptions, and quality issues, ensuring that equipment meets regulatory standards and delivers consistent performance over time.
Reduced Operational Costs
One of the primary advantages of preventive maintenance is its ability to lower operational costs associated with equipment breakdowns, repairs, and replacements. It minimizes the need for emergency repairs, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of equipment, resulting in significant cost savings over the long term. Additionally, by optimizing equipment performance and energy efficiency, preventive maintenance programs help regulated manufacturers minimize utility expenses and enhance overall profitability.
Optimized Resource Utilization
Preventive maintenance programs enable regulated manufacturers to optimize the utilization of maintenance resources, including labor, parts, and inventory. By planning maintenance activities in advance and scheduling them during planned non-production hours, companies can minimize disruptions to daily operations and maximize workforce productivity. Moreover, by maintaining an organized inventory of spare parts and consumables, companies can reduce the lead time for repairs and ensure that maintenance tasks are completed efficiently. This streamlines maintenance workflows and improves overall responsiveness to maintenance needs.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
Regular maintenance and timely repairs provided by preventive maintenance programs can significantly extend the lifespan of equipment and machinery. By addressing wear and tear, lubricating moving parts, and replacing worn components, companies can prevent premature equipment failure and avoid the need for costly replacements.
This not only maximizes the return on investment (ROI) for capital assets but also reduces the frequency of capital expenditures associated with equipment upgrades or replacements. Preventive maintenance programs contribute to long-term sustainability and competitiveness in regulated industries by prolonging critical assets’ operational lifespan.
Prioritizing proactive maintenance practices and investing in the necessary tools, technologies, and training helps manufacturers maintain a competitive edge in highly regulated environments—but, not all preventative maintenance software is made equal.
Selecting the Right Preventive Maintenance Software
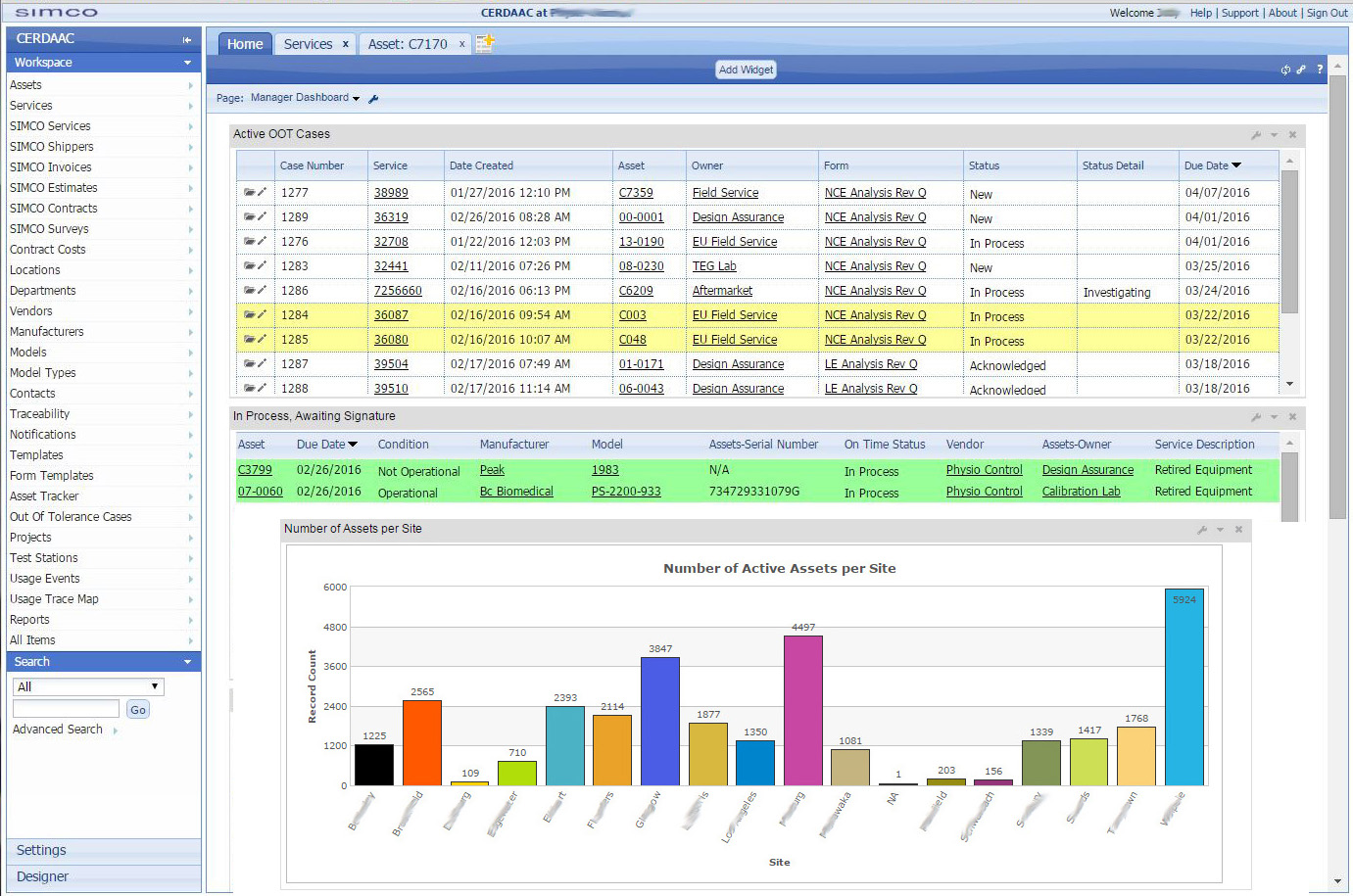
Choosing the appropriate preventive maintenance software is crucial. Here’s how to select the right PM software, focusing on key features and technology considerations:
Look for preventive maintenance software that offers robust scheduling and work order management features. The software should allow users to create and manage maintenance schedules for individual assets or equipment types, set recurring maintenance tasks, and prioritize work orders based on urgency and criticality.
Additionally, the software should support the assignment of tasks to maintenance technicians, provide real-time status updates on work orders, and facilitate communication between team members. Advanced scheduling functionalities, such as automated notifications and calendar integration, can further improve efficiency and accountability in maintenance operations.
Effective asset tracking and management capabilities are essential for maintaining an accurate inventory of equipment, spare parts, and maintenance history. Look for software that allows users to create asset profiles with detailed information, including asset location, specifications, warranty details, and maintenance records. The software should support barcodes, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), GPS (Global Positioning System), or unique asset IDs. These make it easy to identify and track assets and provide visibility into asset performance and reliability metrics.
Comprehensive reporting functionalities are critical for evaluating preventive maintenance programs’ performance and identifying improvement areas. Choose software that offers customizable reporting templates, real-time KPI dashboards, and tools to track key metrics such as equipment uptime, maintenance costs, mean time to repair (MTTR), and mean time between failures (MTBF).
And keep in mind that a cloud-based preventive maintenance software platform offers scalability, flexibility, and accessibility from any device or location with internet connectivity. Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for on-premises infrastructure, reduce IT overhead costs, and ensure seamless software updates and maintenance. They also provide centralized data storage and backup, ensuring data integrity and security.
Invest in a comprehensive software solution that meets the specific needs of regulated manufacturers and integrates seamlessly with existing systems and processes, companies can optimize maintenance operations, minimize downtime, and achieve long-term success in highly regulated environments.
Forward-looking Considerations & Challenges
Integrating the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies is revolutionizing preventive maintenance practices for regulated manufacturers. IoT devices, embedded within equipment and assets, continuously collect and transmit data regarding their performance, health, and operational parameters in real-time. AI algorithms analyze this vast trove of data to identify patterns, predict potential equipment failures, and prescribe proactive maintenance actions.
By harnessing the power of IoT and AI, regulated manufacturers can transition from reactive to predictive maintenance strategies, maximizing asset uptime and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Preventive maintenance also aligns closely with environmental sustainability goals by promoting efficient resource utilization, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact. By implementing proactive maintenance practices, regulated manufacturers can extend the lifespan of equipment, reduce the need for frequent replacements, and optimize energy consumption.
Additionally, preventive maintenance helps identify and address potential environmental hazards or inefficiencies in equipment operation, further contributing to sustainability efforts and regulatory compliance.
But the effectiveness of a preventive maintenance program hinges on its ability to adapt to the unique requirements and operational nuances of each business. Maintenance software that offers customization and personalization capabilities allows regulated manufacturers to tailor workflows, reporting metrics, and maintenance schedules to suit their specific needs. This customization allows companies to align with industry regulations, so manufacturers can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness in maintenance operations.
And then data security and regulatory compliance will continue to be important concerns for regulated manufacturers implementing preventive maintenance programs.
Preventive maintenance software must safeguard sensitive maintenance data with encryption secure data transfers, access controls, and audit trails. Modern CMMS software solutions facilitate compliance with industry regulations such as ISO standards, FDA guidelines, and environmental mandates by providing documentation, audit trails, and automated reporting capabilities. It instills confidence in stakeholders and minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Looking ahead, the future of maintenance is poised to embrace disruptive technologies and transformative trends that will reshape the landscape of preventive maintenance. Emerging technologies such as blockchain hold promise for enhancing asset traceability, ensuring data integrity, and facilitating transparent maintenance transactions.
A CMMS paves the way for regulated manufacturers to embrace the integration of IoT and AI, prioritize environmental sustainability, adopt customization and personalization, ensure security and compliance, and stay abreast of future trends. With CMMS this software as a foundation, regulated manufacturers can create robust preventive maintenance programs that optimize asset performance, mitigate risks, and drive operational excellence in an ever-evolving landscape. Reach out for a demo and we can show you how it looks in action.